Environmental Health advocacy; Occupational Safety; Health Education; Promoting Hygiene and Preventive Health through Workshops; seminars; webinars; Social Media etc Email: EHSadvisor@gmail.com
Sunday, 17 November 2024
NIGERIA NEEDS 11.6M TOILETS TO MEET ODF TARGET – MINISTER UTSEV
Monday, 30 September 2024
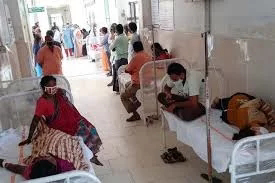
AT LEAST 5 DEAD, MANY HOSPITALIZED AFTER CONSUMING FOOD AT CHURCH EVENT
According to a report by Punch, the tragic incident occurred on Sunday, September 22, 2024, at a church located in the Apata area of Ido Local Government Area, according to reports.
The meal, primarily made of beans, was part of a traditional event known as ‘ipese.’
Health officials at the Infectious Disease Centre in Olodo, Egbeda Local Government Area, where the victims were taken, confirmed the death of five worshippers.
They also noted that numerous others were admitted for emergency treatment.
A health worker at the centre, who spoke anonymously, revealed that about 50 affected individuals had already been treated and discharged. “Some of the victims were brought here for care. So far, 50 have been discharged, and others are still being treated,” the official said.
The Police Public Relations Officer for Oyo State, Adewale Osifeso, also confirmed the incident and stated that investigations are currently underway.
The incident has left the local community in shock, although the exact cause of the deaths remains unclear.
A church member, who requested to remain anonymous, questioned whether the beans dish was the cause of the deaths. “I ate the same meal as everyone else, including the victims, and nothing happened to me,” the source said.
The source further added that various authorities, including the police, DSS, and even the World Health Organization, had been investigating the incident. “Their findings have not yet been released, but I don’t believe the ‘ipese’ is responsible,” they said.
Tuesday, 27 August 2024
WORLD ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH DAY 2024
Theme: 'Environmental Health: Creating Resilient Communities Through Disaster Risk Reduction And Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation.’
Environmental Health is the branch of public health that focuses on the health interrelationships between people and their environments, and promotes human health and well-being by fostering a safe and healthful environment, both built and natural. It encompasses aspects of human health (including quality of life) that are determined by physical, chemical, biological, social and psychological factors in the environment, which include clean air, stable climate, adequate water, sanitation and hygiene, safe use of chemicals, protection from radiation, healthy and safe workplaces, sound agricultural practices, health-supportive cities and built environments, and a preserved nature, which are prerequisites for good health.
World Environmental Health Day was inaugurated in 2011 as an initiative of the International Federation of Environmental Health (IFEH) - a nonprofit organization established in 1986 and based in London, England, which declared 26th September 2011 as the foundational “World Environmental Health Day, ” at its Council's meeting in Indonesia, to raise awareness on the importance of environmental health and to promote actions to protect human health from environmental hazards. The IFEH is a global organization that represents environmental health professionals from over 70 countries, and working to promote best practices in environmental health, while advocating for policies that protect the environment and human health.
World Environmental Health Day has since then been celebrated annually on September 26th as a global observance dedicated to raising awareness about the critical connection between human health and the environment. It is a day to celebrate the work of environmental health professionals who are working to protect the health of the public, and serving as a reminder that the well-being of people is intricately linked to the quality of their surrounding. The theme for this year is,
"Environmental Health: Creating Resilient Communities Through Disaster Risk Reduction And Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation."
Climate Change and disaster risks are fundamental threats to the living and health conditions for all humans on the globe, and in poverty reduction, as well as threat to sustainable development.
Environmental Health plays a critical role in addressing Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation, and Disaster Risk Reduction to create resilient and sustainable communities. Building resilient and sustainable communities requires addressing both climate change and disaster risks, and integrating these risks, as well as potential opportunities, into development planning and budgeting. The scope of work carried out by Environmental Health Professionals, which include handling infectious disease outbreaks, air pollution, water-borne diseases, food safety and security, water pollution, potable water supply, wastewater management, disposal of the dead, vector borne disease control, emergency shelters, ports and border control, hazardous waste, participation in design of emergency planning, engagement in public information on health risks and prevention, involvement in better housing and health, to mention a few, covers a range of interventions needed to address climate change and disaster risks impacts. By driving climate change, initiatives must be strengthened in terms of mitigation and adaption, as climate change and natural hazards driven by it are increasingly going into full-blown disasters.
In Disaster Risk Reduction initiatives and planning for future policy action to promote successful coordination for creation of resilient communities, which include climate change mitigation and adaptation, the needed response to avoid disasters is combatting Climate Change through reduction in the use of fossil fuels and carbon dioxide emission. There is a growing recognition that vulnerability and exposure to disaster risk and climate change impacts are driven to a great deal by social, cultural, economic, and political factors, including multi-dimensional inequalities, discrimination, and marginalization (IPCC, 2014b). Therefore, a reassessment is urgently needed to better integrate disasters, climate change and developmental issues in theory and practice, and enable transformational change on how we foster sustainable development.
Environmental health is important for everyone, but highly essential for vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and people with chronic health conditions. Exposure to environmental hazards can lead to a variety of health problems, including respiratory infections, heart disease, cancer, and birth defects. Environmental Health is a core discipline among lots of other important disciplines, as a concerted and holistic approach is needed in getting this done, both before, during and after disasters. Efforts to reduce disaster and climate change risks have co-existed for a long time, and in the last two decades, they have increasingly been linked, even though negative impacts threaten to obliterate decades of development gains.
The initiatives regarding Disaster Risk Reduction is very much driven by the UN Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. The Sendai Framework works hand in hand with the other 2030 Agenda agreements, including The Paris Agreement on Climate Change, The Addis Ababa Action Agenda on Financing for Development, the New Urban Agenda, and ultimately the Sustainable Development Goals. With all that high-powered coordination, it is expected that all IFEH members and associate members, as well as non members in Environmental Health related institutions or organisations will use this World Environmental Health Day 2024 opportunity to produce initiatives on Environmental Health in general.
On September 26, the world commemorates World Environmental Health Day, with the focus among others on raising awareness on the critical significance of Environmental Health, along with its seven core concepts of Toxicity, Exposure, Dose/Response, Individual Susceptibility, Risks and Benefits, Environmental Justice, and Community Resources and Action. The special day urges collective actions to safeguard human health from environmental hazards. Let’s unite in fostering a global commitment to sustainable practices and environmental stewardship, recognizing that a healthy planet is fundamental to the well-being of present and future generations. Together, we can contribute to a harmonious balance between humanity and the environment.
Credit: QUORA
Jeffrey Whyte Spyda Obadaya